Hadoop伪分布式集群安装配置
本文共 3431 字,大约阅读时间需要 11 分钟。
计算机开发环境:腾讯云云服务器 CentOS 7.6 64位 root用户
基础环境准备:
- Hadoop由JAVA开发,安装配置Hadoop之前需要安装配置JDK,可参考。
- Hadoop监听某些端口,需要将这些端口开放,此处直接关闭防火墙,可参考
- 配置ssh免密登录,可参考
Hadoop下载
访问下载或者键入wget命令下载
wget http://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apache/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.2.1/hadoop-3.2.1.tar.gz
Hadoop解压
键入解压命令,路径自定义
tar -zxf hadoop-3.2.1.tar.gz -C ../software
查看目录检验解压文件
配置环境变量
此处直接配置在root用户下
打开root用户根目录下的隐藏文件.bashrc
vim /root/.bashrc
在.bashrc中输入以下设定配置环境变量
# Hadoopexport HADOOP_HOME=/root/software/hadoop-3.2.1 #路径与自定义路径一致export PATH=$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$PATH
使得.bashrc文件修改生效
source /root/.bashrc
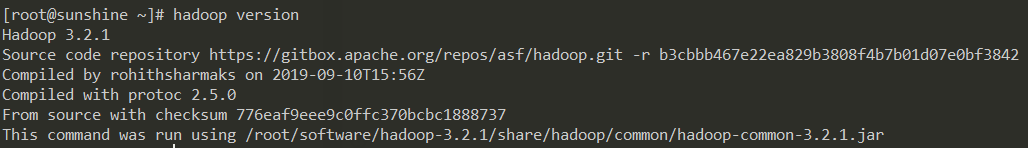
查看Hadoop版本
hadoop version
出现类似如下信息表示配置成功
Hadoop运行文件配置
共有五个配置文件需要相关信息设定以支持Hadoop运行
配置文件位于/root/software/hadoop-3.2.1/etc/hadoop,Hadoop根目录下的ect/hadoop 配置文件一:hadoop-env.sh
配置 hadoop 运行时依赖的 java 环境
将JDK路径添加至该文件,与先前JDK环境配置保持一致,随后保存退出# JDKexport JAVA_HOME=/root/software/jdk-14.0.2 #路径与自定义路径一致
配置文件二:core-site.xml
配置 hadoop 运行过程中临时文件存放的路径及 hdfs 通信方式
将以下代码进行相关修改后粘贴至该文件,随后保存退出fs.defaultFS hdfs://sunshine:9000 hadoop.tmp.dir /root/software/hadoop-3.2.1/tmp
配置文件三:hdfs-site.xml
配置 hdfs 运行时存放的 name 空间元数据和 data 数据块路径
将以下代码进行相关修改后粘贴至该文件,随后保存退出dfs.name.dir /root/software/hadoop-3.2.1/tmp/dfs/name dfs.data.dir /root/software/hadoop-3.2.1/tmp/dfs/data dfs.replication 1
配置文件四:yarn-site.xml
配置 yarn 资源管理相关信息
将以下代码进行相关修改后粘贴至该文件,随后保存退出yarn.resourcemanager.hostname sunshine yarn.nodemanager.aux-services mapreduce_shuffle yarn.nodemanager.vmem-check-enabled false yarn.nodemanager.vmem-pmem-ratio 5
配置文件五:mapred-site.xml
配置 mapreduce 相关所需资源
将以下代码进行相关修改后粘贴至该文件,随后保存退出mapreduce.framework.name yarn yarn.app.mapreduce.am.env HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME mapreduce.map.env HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME mapreduce.reduce.env HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME mapreduce.map.memory.mb 1024
Hadoop namenode 初始化
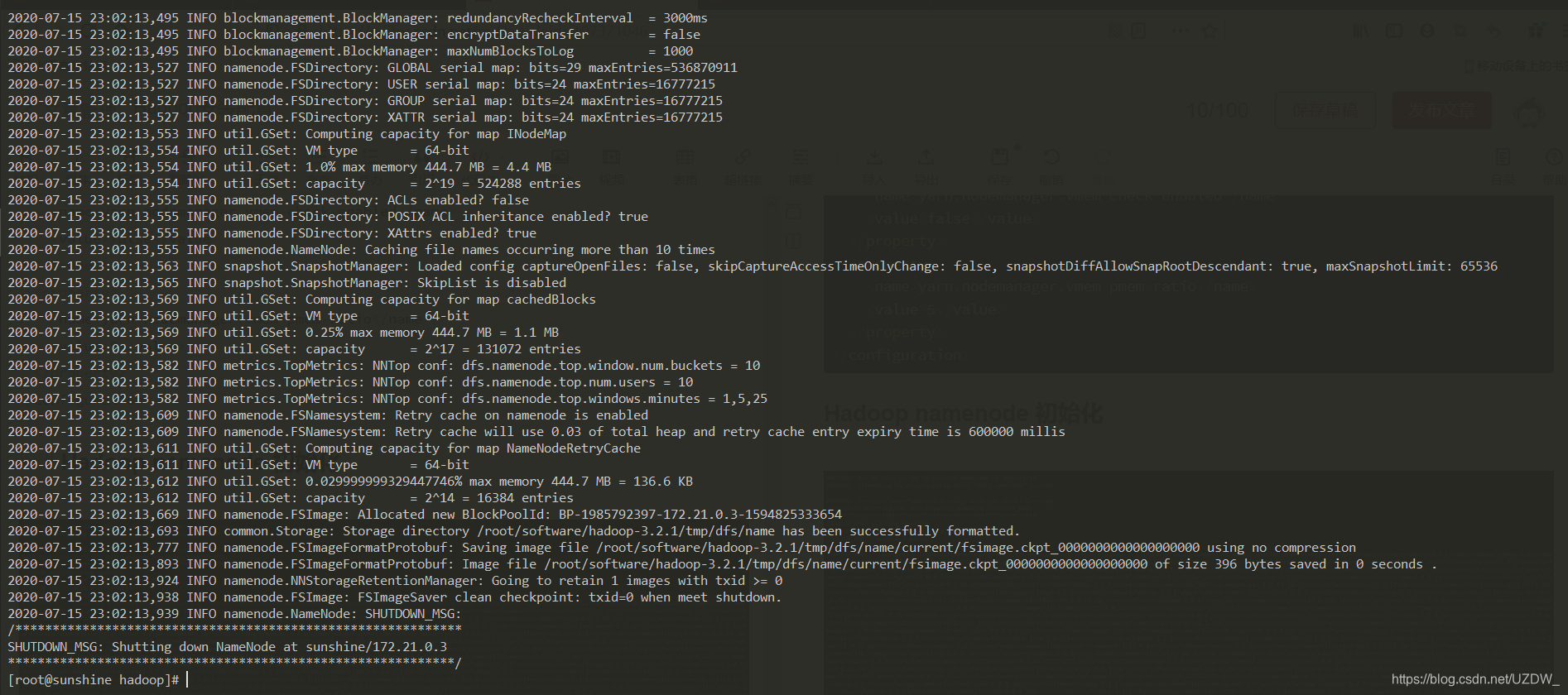
键入初始化命令
hadoop namenode -format
出现如下实例表明namenode初始化成功
启动Hadoop
Hadoop主要的五个进程:namenode、datanode、secondarynamenode、resourcemanager、nodemanager,其中namenode、datanode、secondarynamenode由hdfs提供,resourcemanager、nodemanager由yarn提供。
在目录/root/software/hadoop-3.2.1/sbin下,包含了各个进程的启动和关闭文件  start-all.sh和stop-all.sh分别可以启动全部进程和结束全部进程,键入命令启动全部进程
start-all.sh和stop-all.sh分别可以启动全部进程和结束全部进程,键入命令启动全部进程 ./start-all.sh
随后华丽报错如下
 报错说明没问题,如果在root用户下安装配置Hadoop会出现上述问题,需要额外配置操作,非root用户不需要,操作如下,详细可参考。
报错说明没问题,如果在root用户下安装配置Hadoop会出现上述问题,需要额外配置操作,非root用户不需要,操作如下,详细可参考。 在目录/root/software/hadoop-3.2.1/sbin下
start-dfs.sh和stop-dfs.sh文件,文件顶部粘贴加入以下配置信息 #!/usr/bin/env bashHDFS_DATANODE_USER=rootHADOOP_SECURE_DN_USER=hdfsHDFS_NAMENODE_USER=rootHDFS_SECONDARYNAMENODE_USER=root
对于start-yarn.sh和stop-yarn.sh文件,文件顶部粘贴加入以下配置信息
#!/usr/bin/env bashYARN_RESOURCEMANAGER_USER=rootHADOOP_SECURE_DN_USER=yarnYARN_NODEMANAGER_USER=root
随后重新启动
./start-all.sh
Web端查看
链接如下,ip更改为Hadoop部署机器ip,端口默认9870。
http://119.75.217.110:9870/dfshealth.html#tab-overview
转载地址:http://oehu.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
Mysql 报错 Field 'id' doesn't have a default value
查看>>
MySQL 报错:Duplicate entry 'xxx' for key 'UNIQ_XXXX'
查看>>
Mysql 拼接多个字段作为查询条件查询方法
查看>>
mysql 排序id_mysql如何按特定id排序
查看>>
Mysql 提示:Communication link failure
查看>>
mysql 插入是否成功_PDO mysql:如何知道插入是否成功
查看>>
Mysql 数据库InnoDB存储引擎中主要组件的刷新清理条件:脏页、RedoLog重做日志、Insert Buffer或ChangeBuffer、Undo Log
查看>>
mysql 数据库中 count(*),count(1),count(列名)区别和效率问题
查看>>
mysql 数据库备份及ibdata1的瘦身
查看>>
MySQL 数据库备份种类以及常用备份工具汇总
查看>>
mysql 数据库存储引擎怎么选择?快来看看性能测试吧
查看>>
MySQL 数据库操作指南:学习如何使用 Python 进行增删改查操作
查看>>
MySQL 数据库的高可用性分析
查看>>
MySQL 数据库设计总结
查看>>
Mysql 数据库重置ID排序
查看>>
Mysql 数据类型一日期
查看>>
MySQL 数据类型和属性
查看>>
mysql 敲错命令 想取消怎么办?
查看>>
Mysql 整形列的字节与存储范围
查看>>
mysql 断电数据损坏,无法启动
查看>>